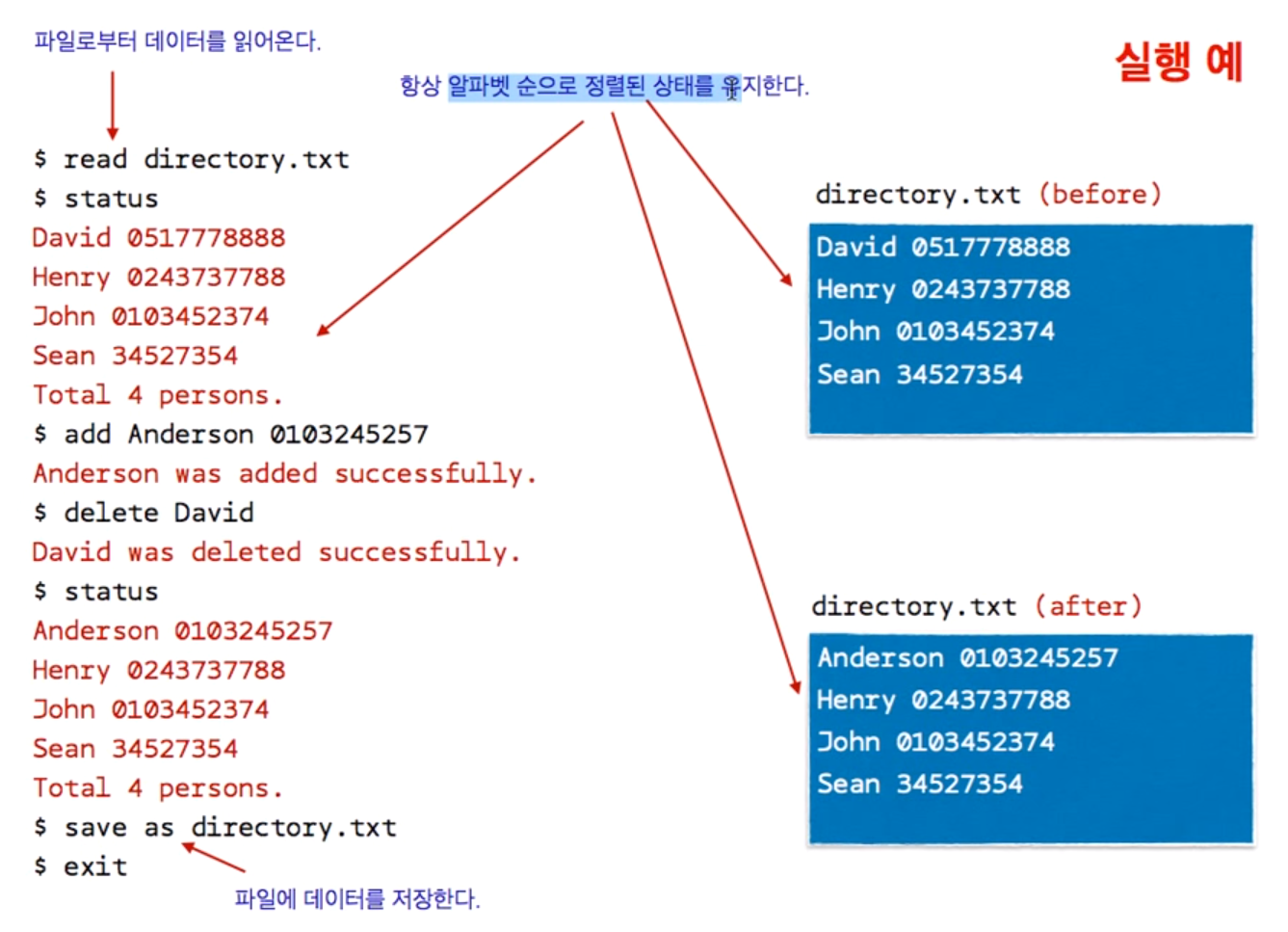
char* numbers[CAPACITY]; // 전화번호는 그냥 '010-1234-5678'같이 문자열로 다루는 게 편함
int n = 0; // 저장되는 사람의 수
void add();
void find();
void status();
void remove();
void load();
void save();
int main()
{
char command[BUFFER_SIZE];
while (1)
{
printf("$ ");
scanf_s("%s", command); // 사용자로부터 명령어를 받음
if (strcmp(command, "read") == 0) // 명령어와 두 문자열을 비교. 두 문자열이 동일하면 0를 리턴
load();
else if (strcmp(command, "add") == 0)
add();
else if (strcmp(command, "find")==0)
find();
else if (strcmp(command, "status")==0)
status();
else if (strcmp(command, "remove")==0)
remove();
else if (strcmp(command, "save") == 0)
save();
else if (strcmp(command, "exit")==0)
break;
}
return 0;
}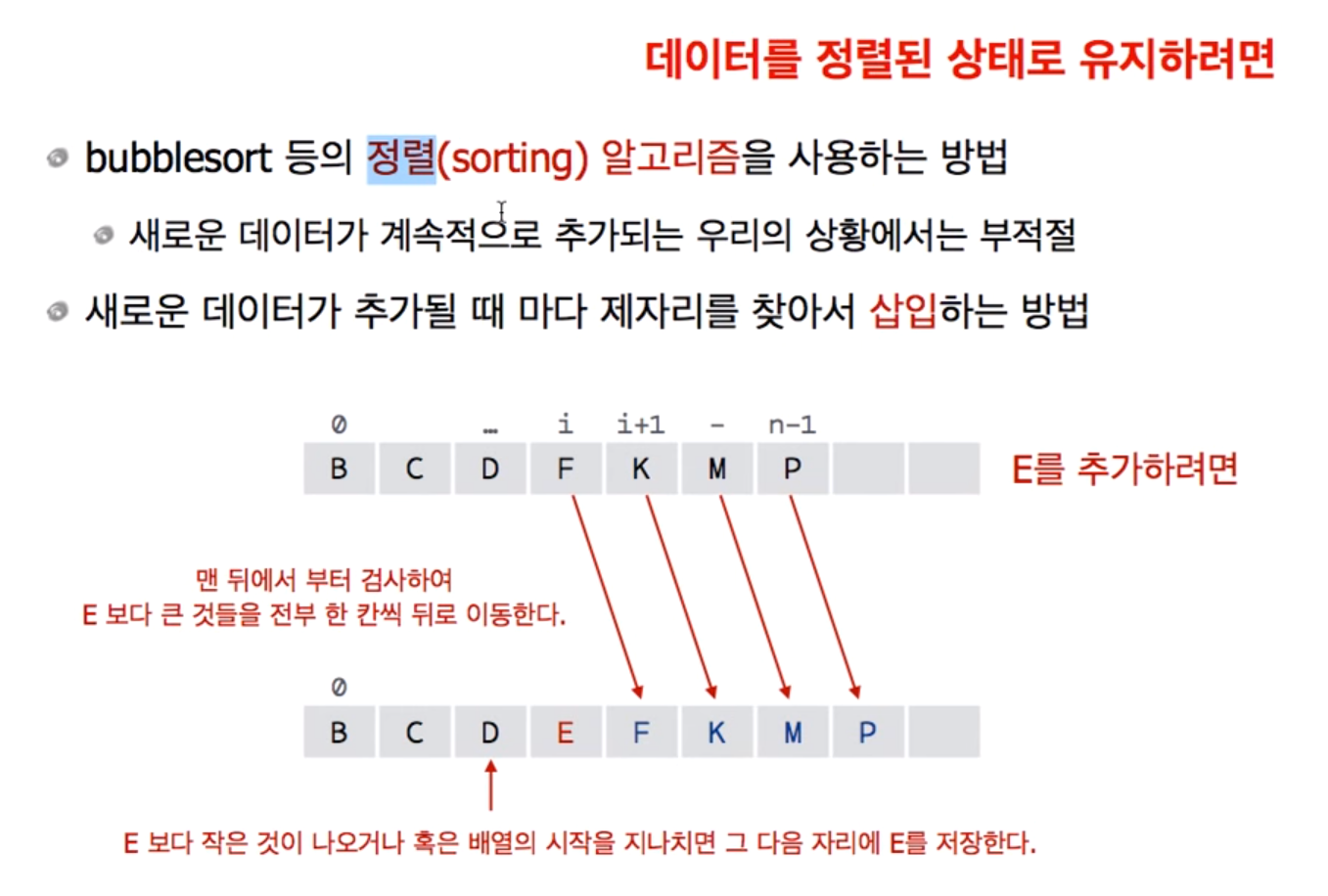
배열의 맨 마지막부터 저장된 값을 E와 비교. E보다 크다면 예외 없이 한 칸씩 뒤로 미뤄줌. 그렇게 계속 E와 비교를 하다가 E보다 작은 값을 마주했을 때 그 인덱스의 바로 뒤에 E를 저장하는 방식
void load()
{
char fileNmae[BUFFER_SIZE];
char buf1[BUFFER_SIZE];
char buf2[BUFFER_SIZE];
scanf_s("%s", fileNmae); // 파일 이름을 읽어옴
FILE* fp = fopen(fileNmae, "r"); // FILE 포인터 타입 변수에 fp 저장. fileName에 저장된 이름의 파일을 "read"모드로 open
if (fp == NULL) // 파일 오픈에 실패했을 때.
{
printf("Open failed.\n");
return;
}
while ((fscanf(fp, "%s", buf1) != EOF)) // EOF 전까지 fp로부터 읽은 이름 데이터를 buf1에 순차적으로 저장
{
fscanf(fp, "%s", buf2); // 이름 데이터와 공백을 두고 띄어서 쓰인 번호 데이터를 buf2에 저장
names[n] = _strdup(buf1); // 배열이 char 변수의 포인터 주소를 저장하기 때문에
numbers[n] = _strdup(buf2); // strdup을 통해 buf의 주소를 리턴받아 배열에 저장
n++;
}
fclose(fp);
}
void save()
{
int i;
char fileName[BUFFER_SIZE];
char tmp[BUFFER_SIZE];
scanf_s("%s", tmp); // save 다음에 저장되는 as를 저장하는 용도
scanf_s("%s", fileName);
FILE* fp = fopen(fileName, "w"); // write 모드로 fileName에 저장
if (fp == NULL)
{
printf("Open failed.\n");
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
fprintf(fp, "%s %s\n", names[i], numbers[i]); // fprintf 함수를 통해 파일 포인터 fp에 문자열 저장.
}
}
void add()
{
char buf1[BUFFER_SIZE], buf2[BUFFER_SIZE]; // 이름과 번호를 저장할 buf1과 buf2
scanf_s("%s", buf1); // 이름을 저장할 버퍼
scanf_s("%s", buf2); // 번호를 저장할 버퍼
int i = n - 1; // 전체 배열의 길이-1. 배열의 마지막부터 비교를 시작함
while (i >= 0 && strcmp(names[i], buf1) > 0) // 두 값을 비교하여 동일하면 0, 앞의 값이 크면 양수, 뒤의 값이 크면 음수 리턴
{ // 사전식 순서로 비교. 대문자가 소문자보다 앞에 위치. 값은 더 작음.
names[i + 1] = names[i]; // 배열의 길이를 증가시켜서 한 칸씩 뒤로 미뤄 저장
numbers[i + 1] = numbers[i];
i--;
}
names[i + 1] = _strdup(buf1); // 이름의 주소를 strdup를 통해 리턴.
numbers[i + 1] = _strdup(buf2);
n++;
printf("%s was added successfully.\n", buf1);
}
void remove()
{
char buf1[BUFFER_SIZE];
scanf_s("%s", buf1);
int index = search(buf1); // search 함수에서 삭제하려는 이름의 인덱스를 찾음. 없다면 -1 리턴
if (index == -1)
{
printf("No person named %s exists.\n", buf);
return;
}
for (int j = index; j < n - 1; j++) // 정렬을 위해
{
names[j] = names[j + 1]; // 삭제된 자리부터 뒤에서 한 칸씩 덮어씌움
numbers[j] = numbers[j + 1];
}
n--;
printf("No person named %s exists.\n", buf1);
}
void find()
{
char buf1[BUFFER_SIZE];
scanf_s("%s", buf1);
int index = search(buf1);
if (index == -1)
printf("No Person named '%s' existes. \n", buf1); // for문을 다 돌았지만 매칭되는 이름을 찾지 못함
else
printf("%s\n", numbers[index]);
}
int search(char* buf)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if(strcmp(names[i],buf)==0)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
void status()
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%s %s\n", names[i], numbers[i]);
}
printf("Total %d people.\n", n);
}'Information Technology > C' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C언어] 전화번호부 v.4 (0) | 2020.01.07 |
|---|---|
| [C언어] 전화번호부 v.3 (0) | 2020.01.06 |
| [C언어] 전화번호부 v.1 (0) | 2020.01.06 |
| [C언어] 문자열(2) (0) | 2020.01.05 |
| [C언어] 문자열(1) (0) | 2020.01.03 |



